What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a programming language that allows us to make web pages interactive. While HTML and CSS only deal with content and style, JavaScript lets us create dynamic interactions like responding to clicks, form submissions, and more.
Integration with HTML
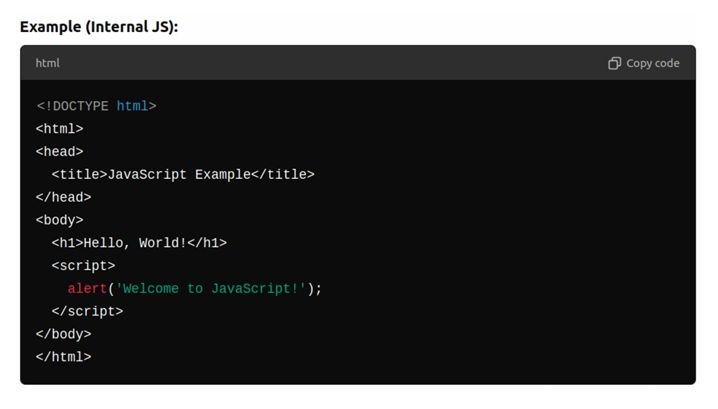
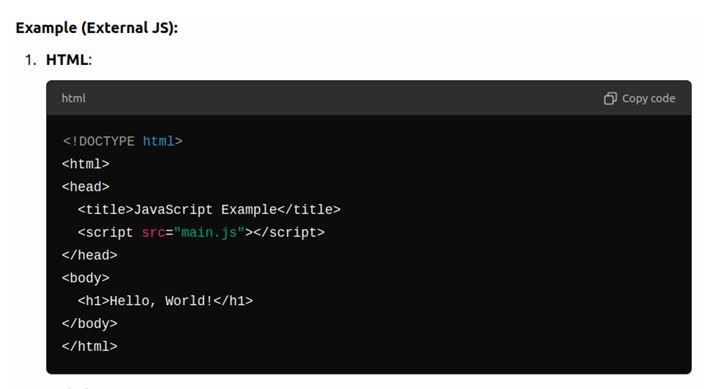
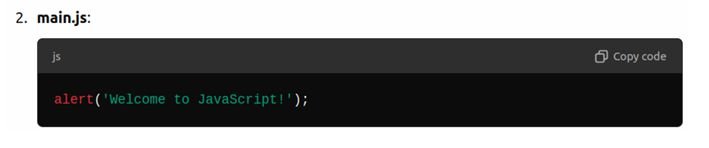
JavaScript can be added to an HTML file either by using a <script> tag within the HTML file or by linking to an external .js file.
Basic Syntax and Structure
Variables in JavaScript
What Are Variables
Explanation: A variable is like a container that stores information we can use later. Just like how you might store books in a box, in programming, we store values (like numbers or words) in variables.
Analogy: Imagine a variable as a labeled box. You can store something inside (like a number, a word, etc.), and whenever you need it, you can retrieve it using the label.
- let name = “Sara”; is like labeling a box “name” and putting “Sara” inside it.
Syntax for Variables:
- Explain the three ways to declare variables:
- let: Used when we might want to change the value later.
- const: Used when the value should stay the same.
- var: Theold way of declaring variables, but we avoid using this now.
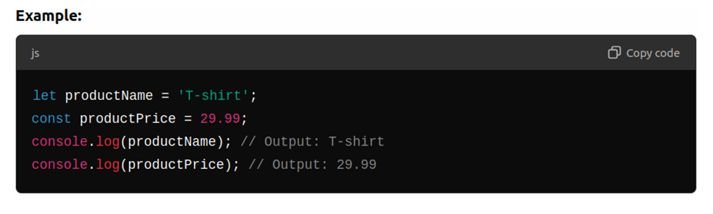
Data Types:
- Strings: Text enclosed in single (‘) or double (“) quotes.
- Numbers: Integers and decimals (e.g., 5, 12.99).
- Booleans: true or false.
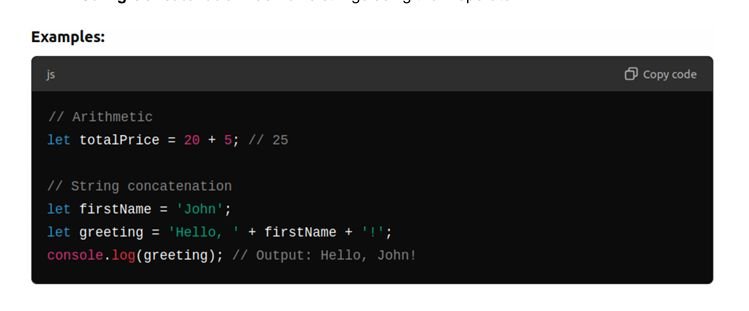
Basic Operations:
- Arithmetic: +,-, *, /, % (remainder).
- String Concatenation: Combine strings using the + operator.
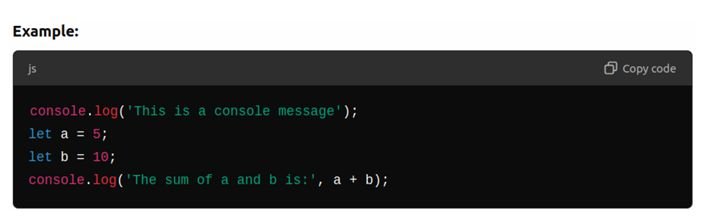
Console Operations:
Using the Console:
The console is a tool that allows developers to output messages, inspect code behavior, and debug.
How to Open the Console
- In Chrome or Firefox, open DevTools (F12 or Ctrl+Shift+I) and go to the Console tab.
- console.log() is used to print output to the console for debugging purposes.
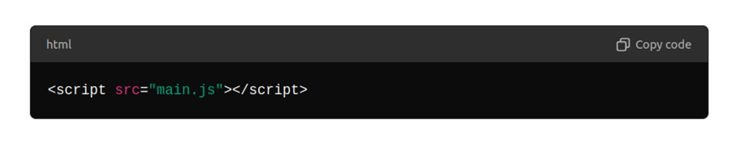
Creating and Linking a JavaScript File
Steps:
- Create a new JavaScript file named main.js.
- Link the JavaScript file to their landing page HTML file.
Conditionals and Functions
Understanding Conditionals:
Conditionals in JavaScript are used to perform different actions based on different conditions. They help the program decide what to do next.
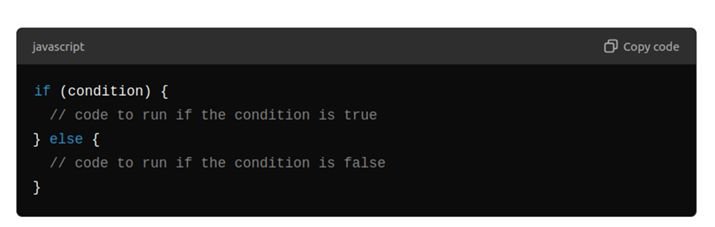
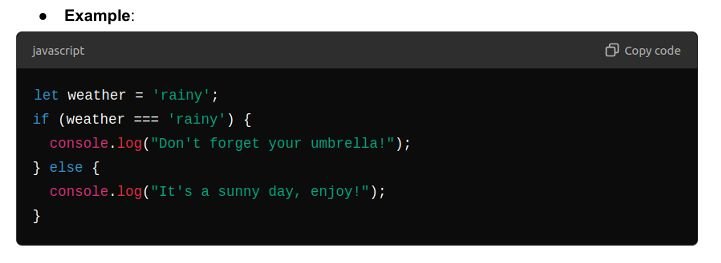
If/Else Statements
Syntax:
Logical Operators:
Explain how to make more complex decisions using operators like == (equality), === (strict equality), > (greater than), < (less than), && (and), || (or), and ! (not).
Introduction to Functions
A function is a reusable block of code designed to perform a particular task, which can be called as many times as needed.
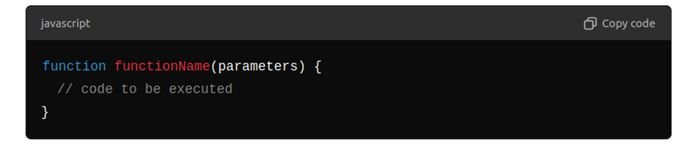
Creating Functions:
Syntax:

Parameters and Return Values
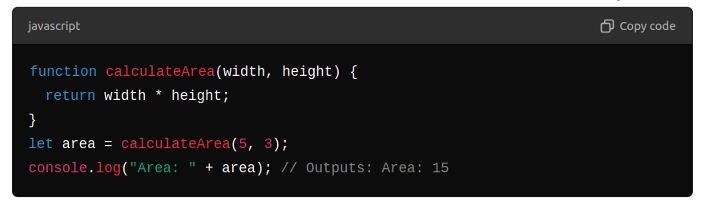
- Parameters are like ingredients for your recipe. They allow you to pass values into functions.
- Return values let you get something back from a function, like the final dish from your recipe.
Example of Parameters and Return Values:
Loops and Basic DOM Manipulation
What is a Loop?
- A loop in programming is a control flow statement that repeats a block of code multiple times based on a condition.
- Think of checking every mailbox in an apartment building one by one; this repetitive action is similar to what loops do in a program.
Types of Loops:
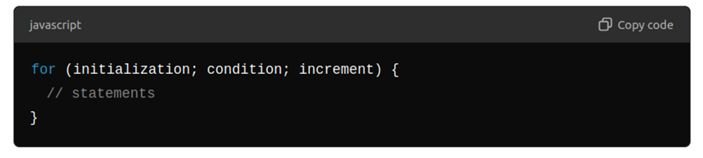
For Loop
- Explanation: Used when the number of iterations is known before the loop starts
Syntax:
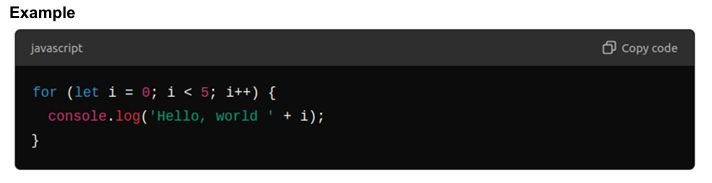
While Loop
- Used when the condition needs to be evaluated before each iteration, and the number of iterations is not known beforehand.
Syntax:

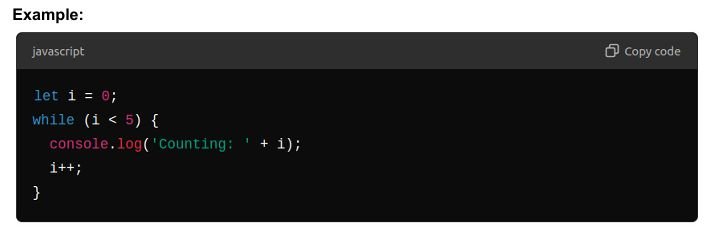
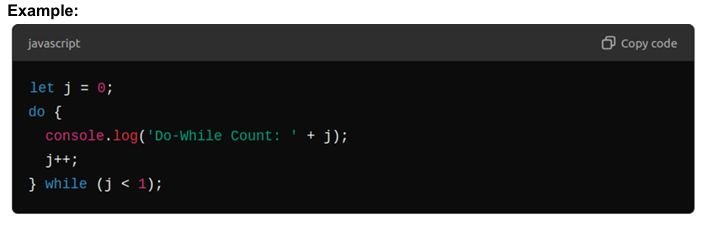
Do/While Loop
- Similar to the while loop, but guarantees that the loop will execute at least once.
Syntax:

Introduction to DOM Manipulation
What is the DOM?
The DOM (Document Object Model) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content.
Diagram/Visual: Provide a simple visual of a DOM tree with elements like ,<html> ,<body>, <div> , <p> and text nodes.
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page. The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects:
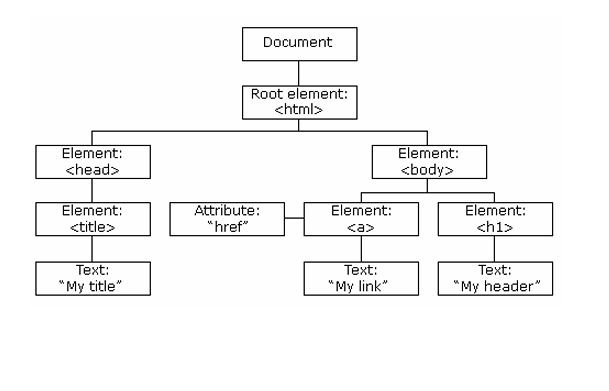
With the object model, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic HTML:
- JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
- JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
- JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
- JavaScript can remove existing HTML elements and attributes
- JavaScript can add new HTML elements and attributes
- JavaScript can react to all existing HTML events in the page
- JavaScript can create new HTML events in the page
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for HTML. It defines:
- The HTML elements as objects
- The properties of all HTML elements
- The methods to access all HTML elements
- The events for all HTML elements
The HTML DOM is a standard for how to get, change, add, or delete HTML elements.
Accessing Elements:
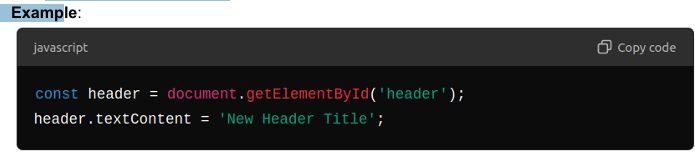
- getElementById:
- Retrieves an element by its ID.
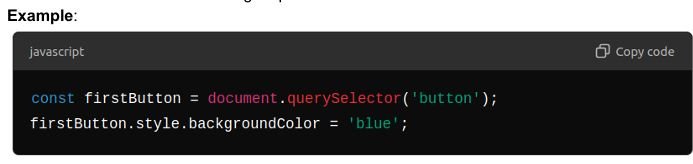
- querySelector:
- Returns the first element matching a specified CSS selector.
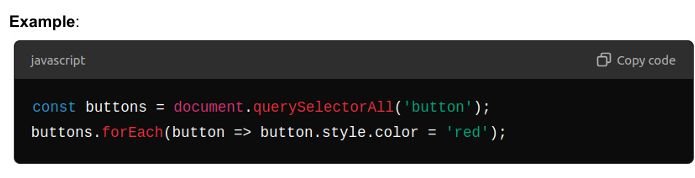
- querySelectorAll:
- Returns all elements matching a specified CSS selector as a NodeList.
Was this tutorial helpful for you please feel free to comment below.