What is HTML?
- HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It’s the standard language used to create web pages.
- HTML is used to structure content on the web by using various tags to define different parts of a webpage.
Basic HTML Document Structure
- Every HTML document starts with a <!DOCTYPE HTML> declaration to tell the browser what type of document it is.
- The main components of an HTML document are:
- <html>: The root element that wraps all the content on the page.
- <head>: Contains metadata about the document, like the title, links to
stylesheets, etc. - <body>: Contains the content that is displayed on the page.
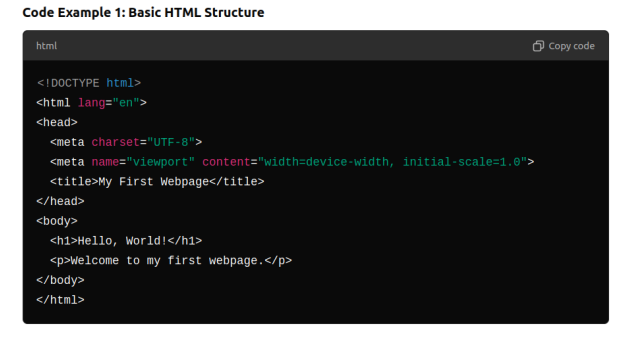
Explanation:
● The <!DOCTYPE HTML>,declaration is a required preamble.
● The <html>,element is the root of the page.
● Inside the <head>, we define the title of the page that appears in the browser tab.
● The <meta charset=”UTF-8”>,sets the character encoding for the document.
● The <body> element contains all the content that will be displayed on the webpage.
Basic HTML Tag
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Lists
- Links
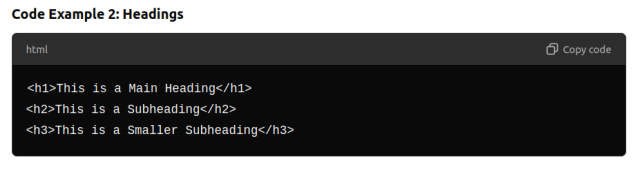
Headings
- HTML provides six levels of headings <h1> to <h6>.
- <h1> is the highest (largest) level heading, and <h6> is the lowest (smallest).
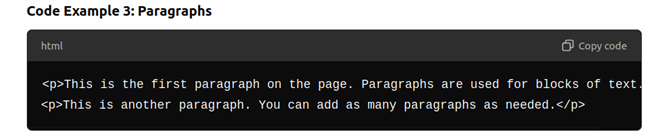
Paragraphs
- Paragraphs are created using the <p> tag. This is used for regular text content
Lists
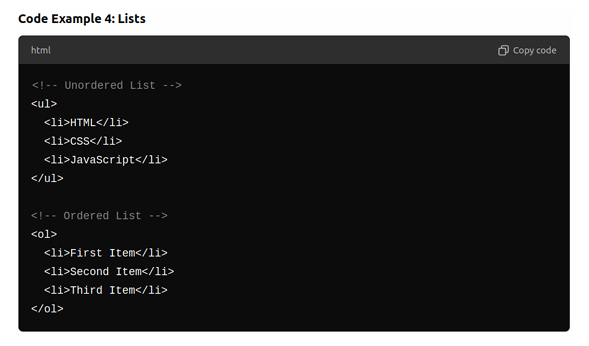
- HTML provides two types of lists: <ul> unordered lists tags and ordered list <ol> tags.
- List items are wrapped inside <li> tags.
Links
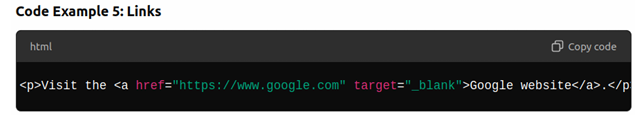
- Links are created using the <a> anchor tag. The href attribute defines the destination of the link.
Example: Google.com, hostinger.com etc.
Attributes and Inline Elements
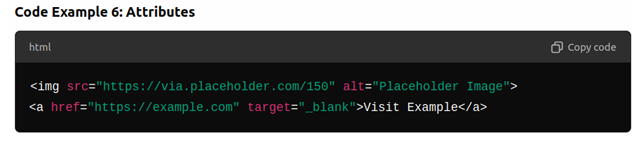
- Explain attributes (e.g., href, src, alt, target).
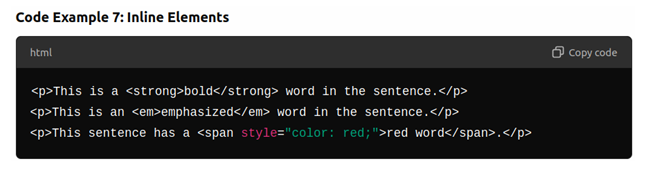
- Introduce inline elements like <span>, <strong> and <em>.
Inline Elements
- Inline elements appear inside other elements without breaking the flow of the document (e.g., within paragraph).
Introduction to Semantic HTML
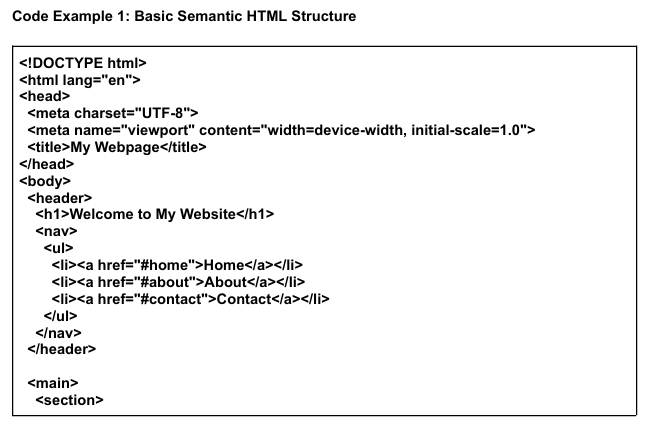
What is Semantic HTML?
- Semantic HTML introduces meaning to the web content. Instead of using generic tags like <div>, semantic elements describe the content in a meaningful way.
- Examples of semantic elements include:
- <header> Represents the header of the page or section.
- <nav> Defines a navigation section.
- <main> Represents the main content of the page.
- <section> A standalone section of related content.
- <footer> Represents the footer of the page or section.

Building a Complete Page Structure
Steps:
1. Header Section:
- Create a <header> element that contains a website title and navigation menu.
- Inside the <nav>, add a list of links <ul> pointing to different sections of the page.
2. Main Content:
- Use a <main> element for the primary content.
- Inside <main>, use <section> tags to divide the content logically (e.g., a product section, service section, etc.).
3. Footer Section:
- Add a <footer> element that includes some footer information (e.g., copyright).
Code Example 2: Creating a Structured Webpage:


Linking Pages Together
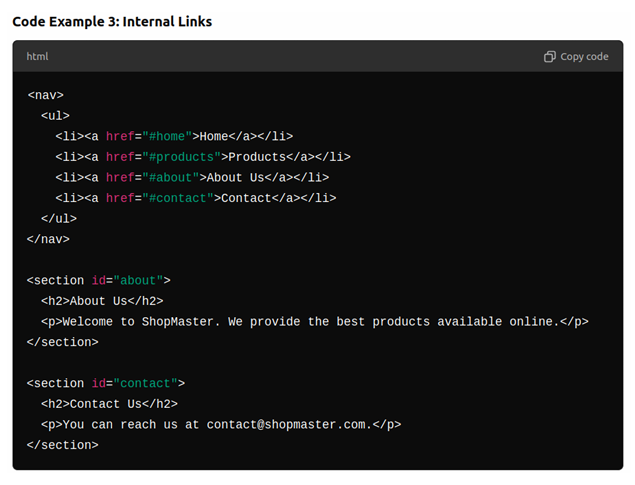
How to Create Internal Links:
- Links <a> elements can link to different sections with in the same page using the id attribute.
- For example ,clicking “About Us” in the navigation should scroll the user to the” About Us” section.

Example:
- Click on the link About Us and you will redirected to our website about us page.